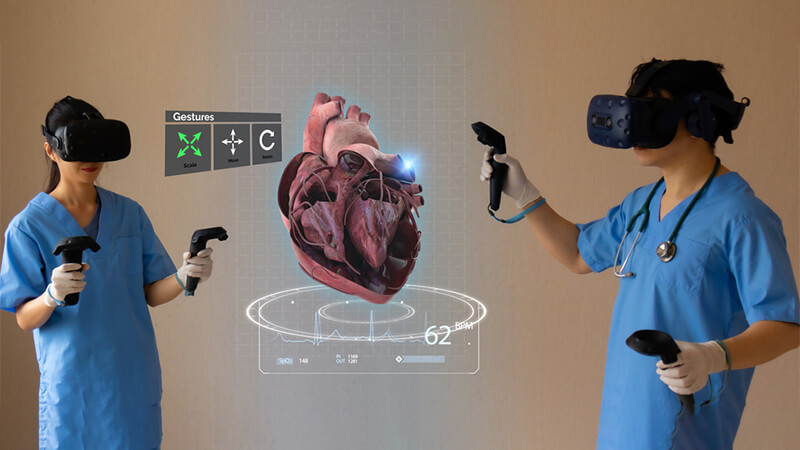
In recent years, Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies have emerged from the realm of science fiction to become tools with significant practical applications, especially in the healthcare sector. With the potential to revolutionize medical training and patient care, AR and VR are setting the stage for a new horizon in healthcare.
For medical training, AR and VR offer an unparalleled opportunity for immersive learning. They allow trainees to navigate through intricate anatomical structures, perform virtual surgeries, and gain exposure to rare conditions, all in a risk-free environment. This hands-on, interactive method of training is proving to be a powerful supplement to traditional didactic teaching, enhancing understanding and retention.
For example, imagine a trainee surgeon practicing a complicated procedure using VR before performing it on a real patient. The VR experience can simulate real-life operating conditions, allowing the surgeon to familiarize themselves with the steps, potential complications, and decision-making process involved in the operation. Such applications can significantly shorten the learning curve for trainees, equipping them with confidence and competence at an early stage in their careers.
AR/VR technologies also offer new avenues for patient care and treatment. They can be used for patient education, enabling individuals to better understand their health conditions and treatment plans. For instance, a doctor could use an AR application to visually demonstrate the impact of a disease on a patient’s body, leading to a deeper understanding and possibly improved adherence to treatment.
Beyond education, VR is gaining traction as a therapeutic tool. Known as VR therapy, this intervention uses immersive experiences to manage pain, support physical rehabilitation, and treat psychological conditions such as phobias and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). In these cases, VR provides controlled environments where patients can safely confront their fears or distract their minds from pain, facilitating healing and recovery.
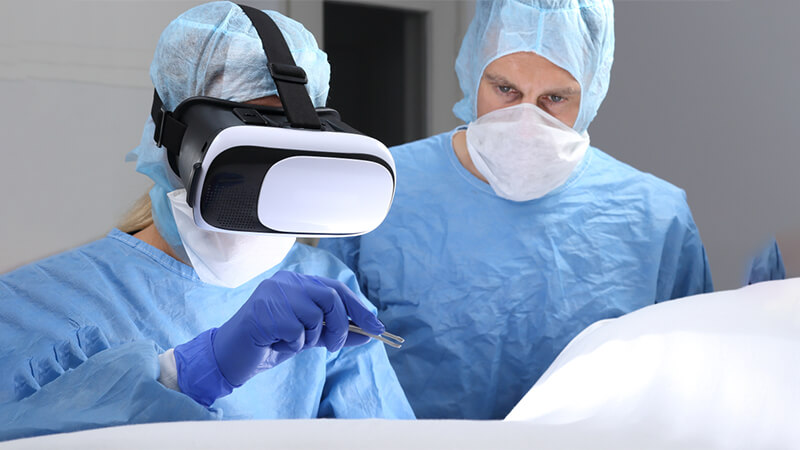
Moreover, AR can play a crucial role in surgeries and other complex procedures. Surgeons can overlay AR images onto the patient’s body to visualize the underlying structures, improving precision and outcomes. For example, in a process known as “AR-assisted navigation,” a surgeon can see the precise location of a tumor or a blood vessel on a screen while operating, enhancing accuracy and minimizing risks.
However, while the potential of AR/VR in healthcare is exciting, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges. High-quality AR/VR experiences require significant resources, including advanced equipment and specialized skills. Additionally, there are questions about data security, user comfort, and the potential for misuse of these technologies.
As we explore this new frontier, it’s crucial to ensure that ethical considerations and the needs of all users, including healthcare professionals, patients, and students, are at the forefront. In doing so, we can maximize the benefits of AR and VR technologies while minimizing the risks, ushering in a new era of healthcare that is more immersive, personalized, and effective than ever before.